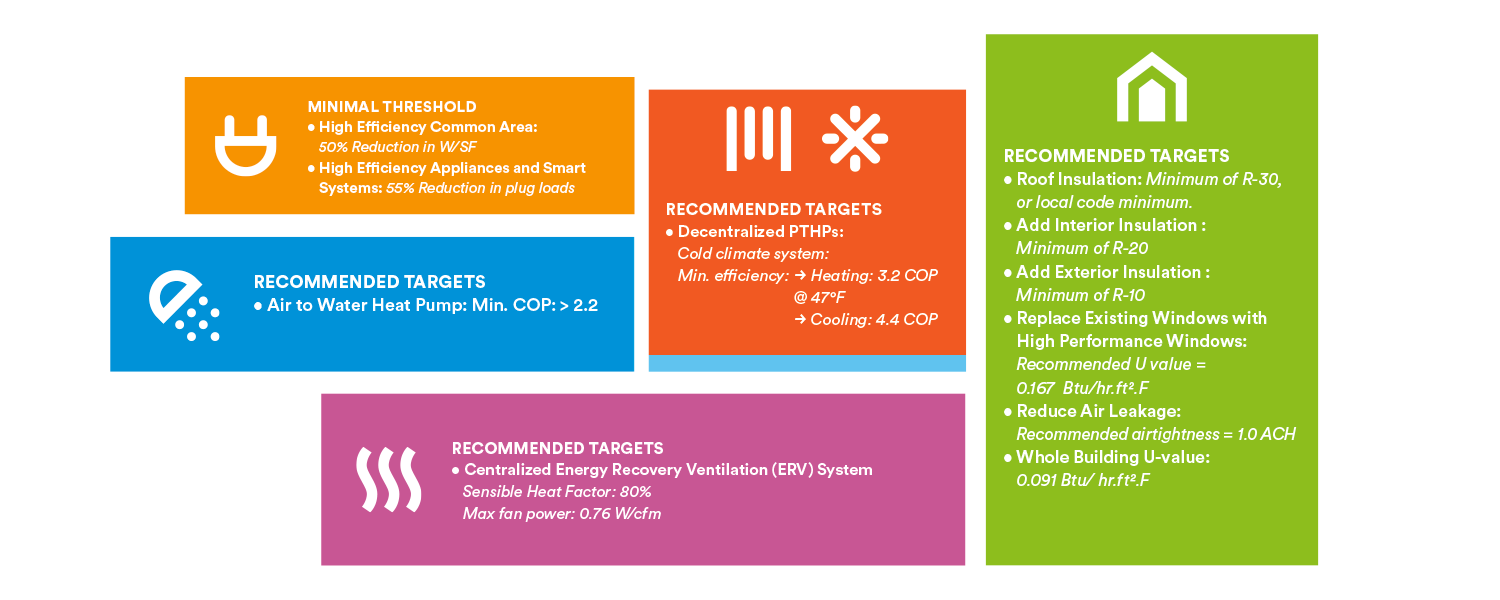
Post-1980 8+ Stories
This playbook summarizes retrofit strategies that maximize occupant comfort and energy savings through a transition from fuel to electricity- based heating, cooling and hot water systems. Aligned with typical capital improvement cycles, the recommendations will prepare buildings for increasingly stringent efficiency and carbon emissions targets through careful phasing of work across all major building components, including upgrades to exterior walls, windows, and ventilation systems.
Post-1980 Mid- to High-Rises are typically at a minimum of 8 floors in height and can be found in virtually every context–from lot line buildings, to free standing buildings on campuses. Many buildings of this type include mixed uses at the ground floor, such as retail (grocery stores, pharmacies, etc.) and commercial offices (Doctor’s offices, etc.). Tenant amenities are common, such as laundry, gym, lounge, rooftop terrace, and storage.
The post 1980s mid to high rise building selected for study is a 16-story, market-rate residential building on Roosevelt Island in New York City. The building has large glazing areas with perimeter columns that have interior insulation and an exterior masonry rain screen. The building is comprised of 242 apartments across roughly 242,000 gross square feet.

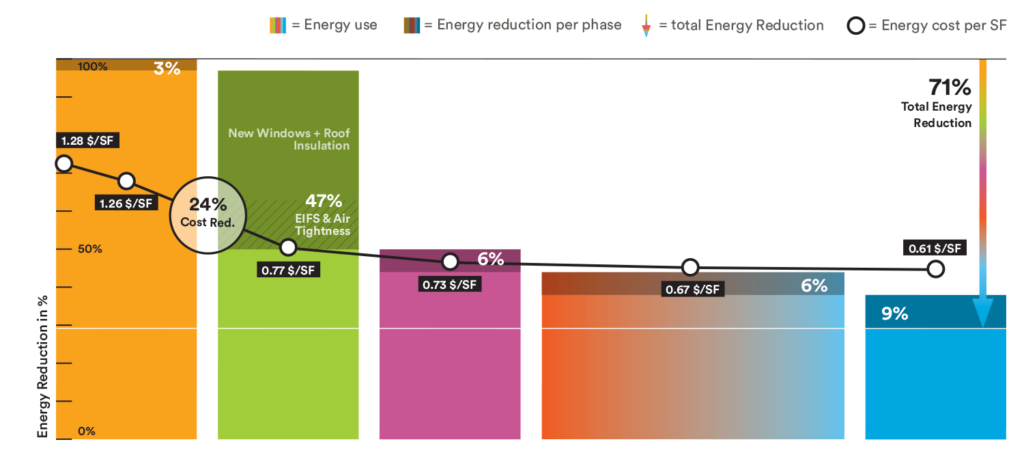 Shown left to right: Lighting & Loads, Envelope, Ventilation, Heating & Cooling, and Domestic Hot Water.
Shown left to right: Lighting & Loads, Envelope, Ventilation, Heating & Cooling, and Domestic Hot Water.